How Do Eye Doctors Diagnose Vision Problems?
Understanding how eye doctors diagnose vision problems is crucial for maintaining optimal eye health. Timely diagnosis not only helps in effective treatment but also plays a vital role in preventing further complications that could lead to vision loss. Let's take a moment to delve into the comprehensive methods and tools eye care professionals utilize to accurately diagnose a wide range of vision issues.
Comprehensive Eye Examination
Visual Acuity Test
Visual acuity tests are pivotal as they measure the sharpness of your vision, often using standardized eye charts. This test determines how well you can see letters or symbols from a distance, allowing eye doctors to assess the clarity of your vision under different conditions. Eye charts with rows of progressively smaller letters help establish the smallest size you can read without significant strain. Regular visual acuity tests are vital, as they can indicate changes in visual clarity that might necessitate corrective lenses. Early detection of issues here is critical as it sets the stage for further diagnostic procedures to refine the nature of any problems.
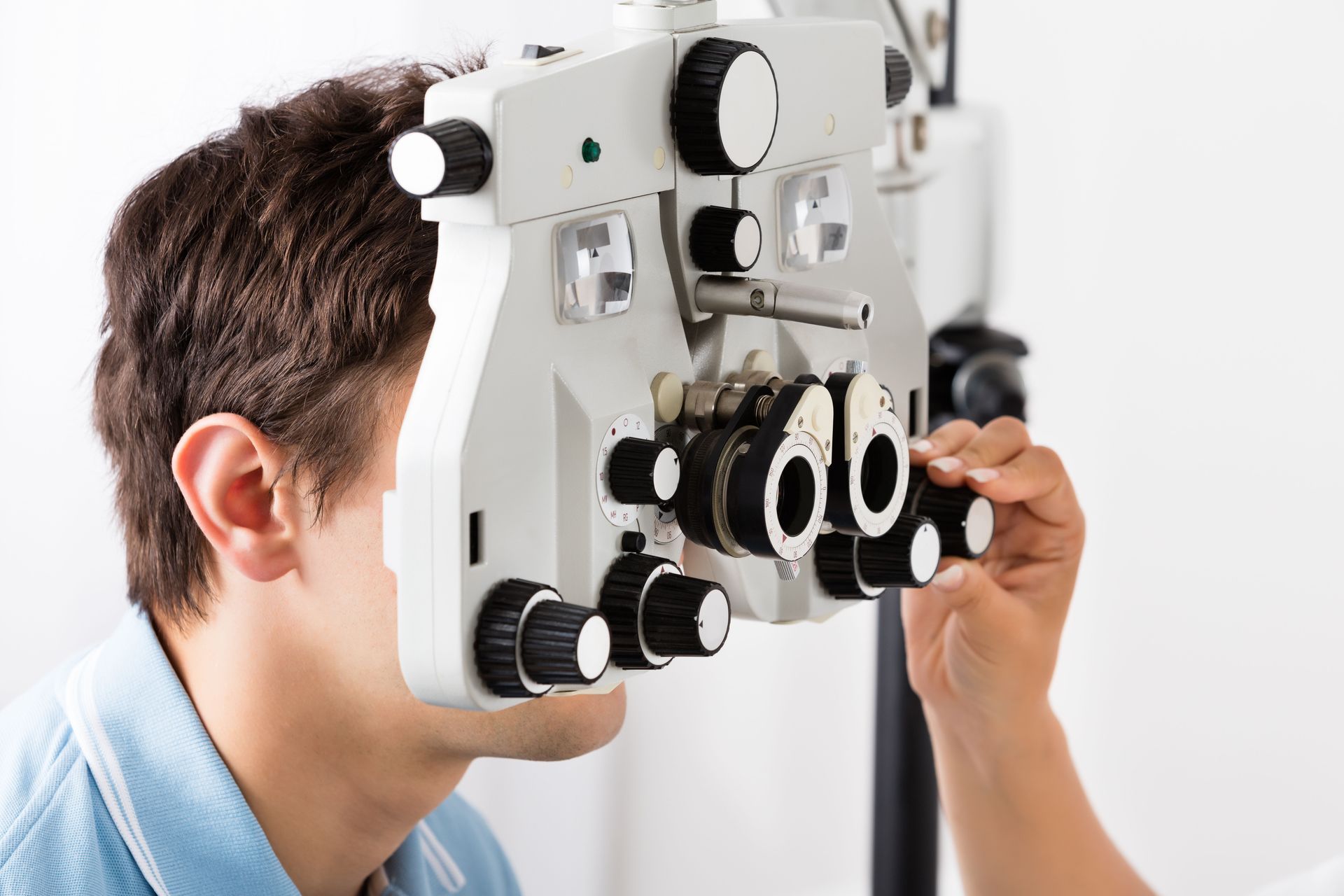
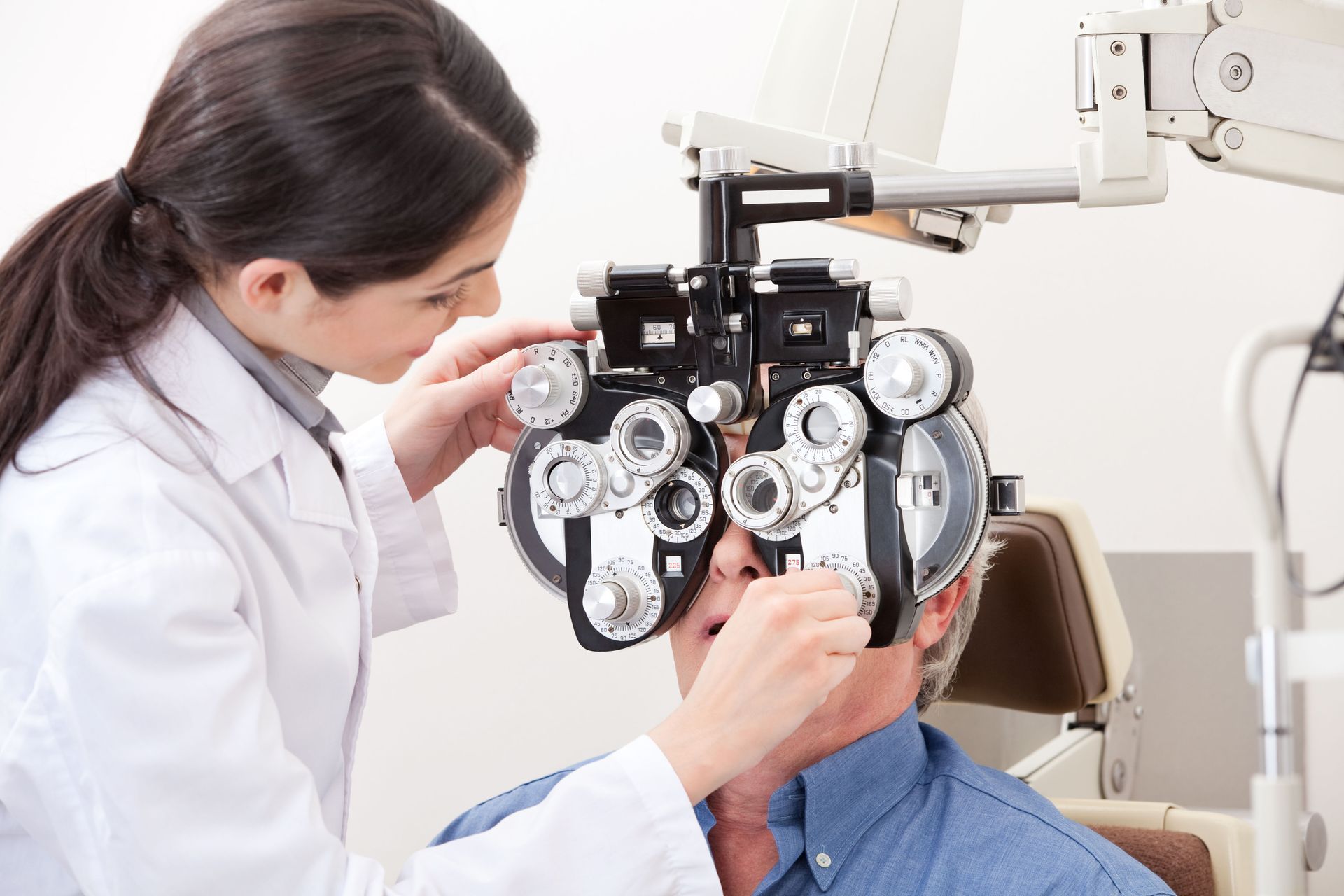
Refraction Test
The refraction test is a key component in determining the exact prescription needed for glasses or contact lenses. By systematically altering lenses while the patient views an eye chart, eye doctors pinpoint specific refractive errors. This test helps in identifying conditions such as myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Accurate refraction findings are essential for crafting eyeglasses or contacts that can significantly enhance one's quality of life. Modern refractive assessments have become more sophisticated, with devices offering increased accuracy in identifying even minor vision deviations.
Eye Muscle Function Test
The eye muscle function test assesses the efficiency of the muscles controlling eye movement. Each eye has six muscles that control its movement, and this test ensures they work harmoniously. Discrepancies in muscle function can lead to issues such as strabismus, where the eyes don't look in the same direction simultaneously. Proper muscle coordination is imperative for stable and unobstructed vision, as misalignment can affect depth perception and focus. Understanding and correcting muscle function is essential in maintaining visual stability and comfort.
Pupil Dilation
Pupil dilation is an essential procedure allowing ophthalmologists a better view of the internal structures of the eye. By using special eye drops to widen the pupil, doctors can inspect the retina, optic nerve, and other crucial components. While the process requires some minutes for the medication to take effect, the improved view is quintessential for a comprehensive ocular health assessment. Once dilated, any abnormalities, such as tears or detachment, or signs of diseases like macular degeneration, become more apparent. Though temporarily affecting vision, the diagnostic advantages significantly outweigh the minor inconveniences.
Ocular Health Assessment
An ocular health assessment evaluates the overall condition of the eye, looking beyond simple vision problems. This part of the exam includes the retina, optic nerve, and lens, checking for signs of disease or damage. Modern diagnostics have equipped eye doctors with advanced tools that enhance their diagnostic capabilities, much to the preference of patients. According to VisionCenter.org, around 80% of patients favor practices that employ state-of-the-art diagnostic tools. This preference underscores the importance of continuous advancements in the precision and reliability of ocular health assessments.
Imaging and Diagnostic Tools
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical Coherence Tomography, or OCT, is a cutting-edge imaging technique that provides high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina. OCT is instrumental in diagnosing and monitoring the progression of macular diseases, such as macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy. Through detailed imaging, OCT allows doctors to detect changes in retinal thickness, layers, and surface contours. This non-invasive procedure relies on light waves and can reveal details that are otherwise invisible to traditional examination methods. As eye health technology advances, OCT remains a cornerstone in the early detection and treatment planning for various retina-related conditions.
Fundus Photography
Fundus photography involves capturing detailed photographs of the interior surface of the eye, including the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels. This imaging technique aids in documenting the eye's health, allowing for accurate comparisons over time during follow-up visits. Fundus photography is particularly useful in identifying issues such as retinal detachment, optic nerve damage, or retinal vasculature changes. As these images provide a permanent record, they are invaluable for tracking the progression of chronic conditions or monitoring responses to treatment. The clarity and detail achieved through fundus photography enable precise diagnostic and therapeutic decisions.
Visual Field Test
The visual field test measures peripheral vision and can detect blind spots or reductions in the visual field. This test is crucial in the early detection of glaucoma, a condition that can cause irreversible vision loss if not diagnosed and managed promptly. During the test, patients respond to lights or patterns appearing in their peripheral vision while maintaining focus on a central point. By mapping the visual field, eye doctors can identify areas of vision loss and diagnose potential underlying conditions. Reliable visual field testing helps construct a comprehensive understanding of patient vision, enabling tailored intervention strategies.
Common Diagnostic Procedures
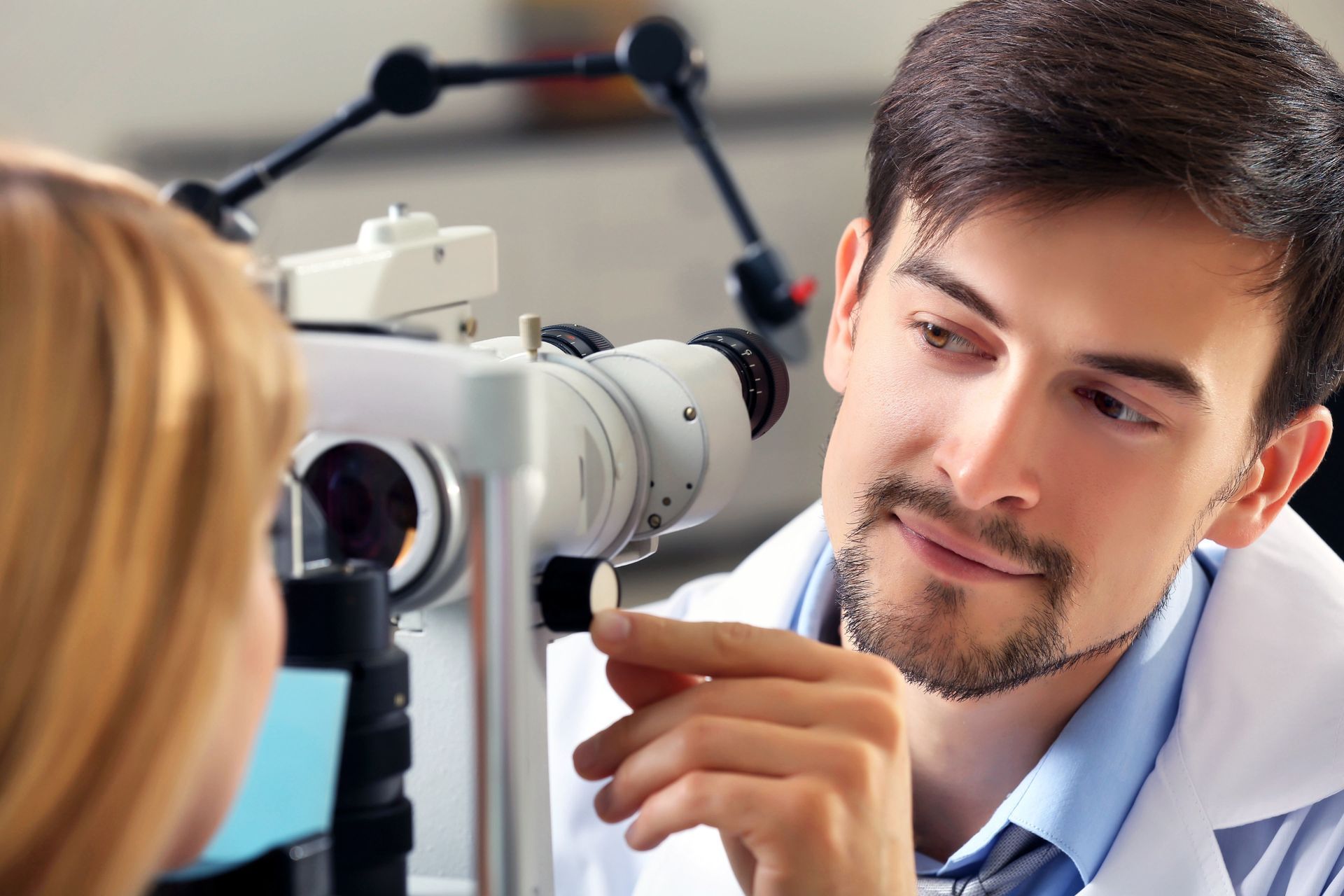
Slit Lamp Examination
The slit lamp examination evaluates the structures at the front of the eye, including the cornea, iris, and lens. Using a high-intensity light source and a binocular microscope, ophthalmologists can magnify and inspect these areas for abnormalities. This procedure detects signs of cataracts, corneal injuries, or uveitis, among other conditions. A slit lamp test is often complemented by additional diagnostic measures, ensuring a robust and thorough analysis of anterior eye health. Early identification of structural anomalies provides the best opportunity for timely intervention and management, preserving vision and preventing further complications.
Tonometry
Tonometry is the process of measuring the intraocular pressure of the eye, a critical indicator in diagnosing glaucoma. Abnormally high pressure within the eye could indicate potential optic nerve damage, making early detection paramount. The test can be performed using different methods, each designed to provide reliable and accurate measurements of eye pressure. Regular tonometry screenings are integral for patients at risk of glaucoma, ensuring any changes are promptly addressed. By identifying increased pressure early, treatment plans can be developed to manage pressure levels and prevent vision loss.
Diagnosing Refractive Errors
Myopia Detection
Myopia, or nearsightedness, is diagnosed when individuals have difficulty seeing distant objects clearly. It often arises during childhood, progressing until eye growth stabilizes. Eye exams revealing myopia typically involve refraction assessments and visual acuity tests. As myopia becomes increasingly prevalent globally, prompt diagnosis and management are essential to prevent further deterioration and complications. Corrective measures, such as glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery, address this refractive error effectively, providing clearer distant vision.
Hyperopia Identification
Hyperopia, or farsightedness, occurs when distant objects are seen more clearly than near ones, often resulting in eye strain or headaches. During an eye exam, refraction tests reveal hyperopia by determining the optical power needed to correct vision. Detecting hyperopia early is important, especially in children, as it sometimes affects reading and learning abilities. Options for correction include lenses with convex curvature or advanced refractive surgeries, improving near vision and reducing strain. Awareness and timely detection allow eye care professionals to implement suitable corrections that enhance visual comfort and performance.
Astigmatism Assessment
Astigmatism occurs when the eye does not focus light evenly on the retina, leading to distorted or blurred vision. Routine eye exams can detect astigmatism through a combination of visual acuity tests and refractive assessments. The condition often coexists with myopia or hyperopia, necessitating comprehensive refraction tests to establish an accurate prescription. Corrective lenses or specialized contact lenses address astigmatism effectively, enabling clearer vision. Recognition and treatment of astigmatism ensures patients gain full restorative benefits, minimizing visual distortions.
Understanding the methods to diagnose vision problems highlights just how thorough and precise modern eye care has become. From visual acuity and refraction tests to advanced imaging technologies like OCT and fundus photography, each diagnostic tool plays a crucial role in identifying both common refractive errors and more serious ocular conditions. Regular comprehensive eye exams allow for early detection and intervention, helping patients maintain clear vision and overall eye health. By staying proactive with eye care by visiting eye doctors at Optical City, you can protect your sight, prevent complications, and enjoy a higher quality of life. Reach out today to get started with our care!



Share On: